

How the Fashion Industry Can Embrace Circular Economy: Insights from the WBCSD's Latest Sector Guidance
The fashion industry, a significant contributor to environmental and economic challenges globally, stands at the cusp of a transformative journey towards sustainability. The World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) has recently published a comprehensive guide aimed at steering the sector toward a more circular and resilient future. This guide outlines the practical steps needed to implement circular economy principles, and also highlights the shared responsibilities of various stakeholders in the fashion value chain.
The WBCSD's guidance underscores the urgent need for the fashion industry to move away from the traditional 'take-make-waste' model, which contributes extensively to pollution and resource depletion. Instead, it advocates for a circular system where materials are not merely recycled, but where the entire lifecycle of a product is considered — from design through to end-of-life. This approach promises both environmental benefits and significant economic opportunities, from reducing waste to creating innovative revenue streams.
Key Strategies for Circular Fashion
The guidance identifies several key areas where fashion businesses can initiate their circular transition:
-
Design for Longevity: Designing products that are meant to last longer and can be easily repaired or recycled is foundational. This includes selecting durable, sustainable materials and designing for easy disassembly.
-
Sustainable Business Models: The guide encourages the exploration of business models that focus on services like renting, sharing, or reselling, which keep clothes in use longer and reduce the need for new productions.
-
Enhanced Material Flows: By improving material flows through better sorting, collection, and recycling processes, the industry can significantly cut down on waste and the demand for virgin resources.
-
Cross-Sector Collaboration: Collaboration across different sectors and industries is crucial for developing new technologies and systems that facilitate circular practices, such as material traceability and recycling technologies
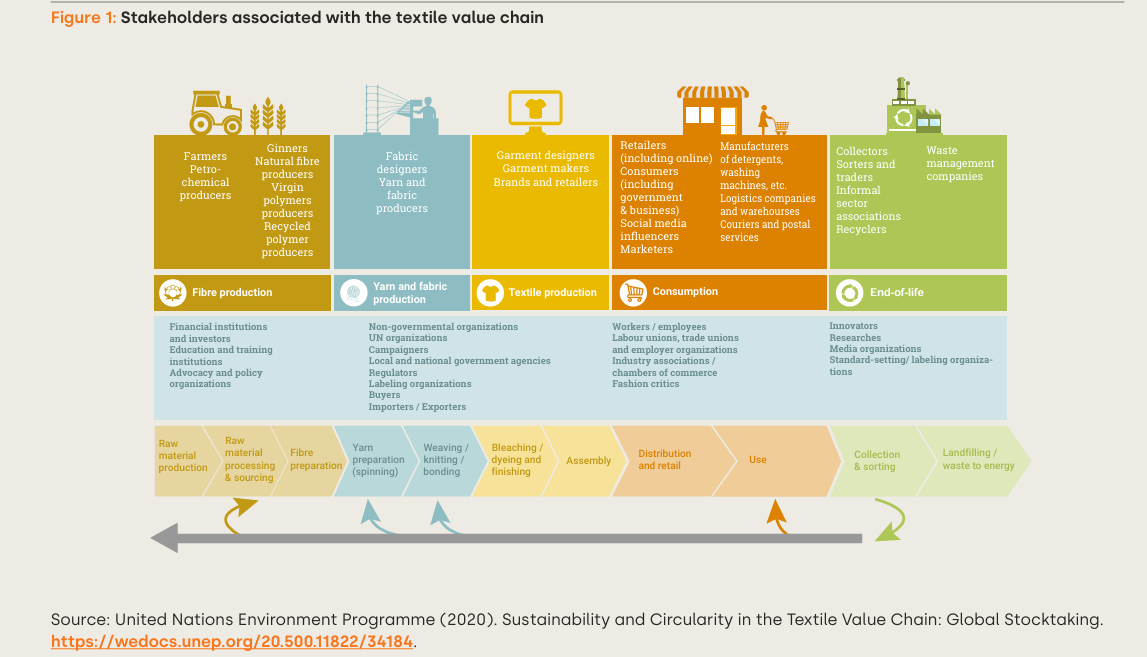
Stakeholders associated with the textile value chain
(Retrived from CTI_fashion_initiative_sector-guidance_WBCSD.pdf)
Implementing the Transition
The WBCSD report provides a roadmap for implementation, suggesting that each organization needs to assess its current position in the circular economy, set clear targets, and measure progress. It highlights the importance of transparency and accountability, suggesting that sharing progress and challenges not only fosters trust but also encourages industry-wide learning and improvement.
"Ambitious circular goals require substantial investment, impactful actions and the monitoring of results. Using quantitative metrics and data driven insights can help companies attract investments and report credibly on their progress on circularity."
The Role of Policy and Consumer Awareness
Regulations on sustainability performance and circular design for fashion are growing worldwide. Achieving a circular fashion industry is not solely the responsibility of the companies involved. The guidance stresses the role of policymakers in creating conducive environments for circular practices through regulations and incentives. Equally, it points out the necessity of increasing consumer awareness and demand for circular and sustainable fashion, which can drive change from the market side.

Picture source: AI-generated
Conclusion
The circular transition in the fashion industry is an ambitious yet necessaryt endeavor. By following the WBCSD's sector guidance, businesses can take practical and impactful steps towards a more sustainable and circular future. Not only does this transition promise to mitigate the environmental impact of one of the world's most pollutive industries, but it also offers a pathway to innovative business practices that can lead to economic growth and sustainability in harmony.
The WBCSD's Circular Transition Indicators (CTI), with metrics specifically designed for the fashion industry, significantly enhance the circular economy's scalability. The CTI provides a detailed and adaptable framework for measuring circularity, accessible to businesses across all sectors and sizes.
This strategic framework presented by the WBCSD acts as a guiding light for every participant in the fashion industry, from emerging designers to established multinational corporations, who wish to be a part of this circular transition.
Sources:

Finanziato dall'Unione europea. Le opinioni espresse appartengono, tuttavia, al solo o ai soli autori e non riflettono necessariamente le opinioni dell'Unione europea o dell’Agenzia esecutiva europea per l’istruzione e la cultura (EACEA). Né l'Unione europea né l'EACEA possono esserne ritenute responsabili.
